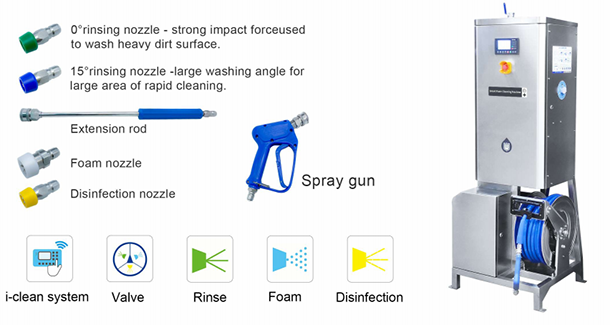
How to set foam cleaning in a 5000-square-meter food workshop?
For large food production workshops with an area of 5000 square meters, the scientific and efficient configuration of foam cleaning points is crucial to
ensuring overall hygiene, improving cleaning efficiency, and controlling operating costs. The configuration plan is not simply about evenly distributing the
area; it requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors, including workshop layout, production processes, hygiene level zoning, equipment type,
and investment budget.
I. Two Mainstream Foam Cleaning Equipment Types
01-325M
Coverage and Deployment: Highly flexible. Points can be distributed throughout the 5000 square meter workshop as needed, with each unit covering the
surrounding area. Depending on the layout, 3-5 points can be set up within the 5000 square meter workshop.
.png)
.png)
Independence: Each point operates completely independently; a failure in one unit will not affect other equipment.
Cleaning Flexibility: Each cleaning point can be independently configured with different cleaning programs, pressures, and chemical concentrations to
adapt to different area needs (e.g., high-concentration alkaline solutions for heavily oiled areas).
Chemical Management: Concentrate containers must be placed next to each piece of equipment for on-site storage; management points are dispersed.
Pipelining Engineering: Simple; only low-pressure water pipes, compressed air pipes, and electrical circuits need to be laid for each point.
Initial Investment: Low. Purchases can be made in batches as needed, minimizing initial investment pressure.
Energy Consumption: Low. Only single-unit operation is required during use.
Suitable Scenarios: Suitable for workshops with complex layouts, multiple zones, varying cleaning needs across areas, and where phased investment or
future layout adjustments are desired (e.g., 5000 square meter workshops).
02-325E
Coverage and Deployment: Fixed-point coverage; requires wall mounting; coverage radius approximately 25 meters (standard 25-meter hose included).
_54242.png)
_69489.png)
Independence: Completely independent; failure at one point does not affect other points.
Cleaning Flexibility: High; each cleaning point can be independently configured with different cleaning programs, pressures, and concentrations.
Chemical Management: Decentralized on-site management; concentrate containers are placed in the equipment's chemical tank for on-site storage and
replacement.
Pipelining Engineering: Simple; only low-pressure water pipes, compressed air pipes, and electrical circuits are required for each point.
Initial Investment: Low; cost is limited to the unit purchase and associated piping.
Energy Consumption: Low; power is only consumed during operation.
Suitable Scenarios: Suitable for medium to large-sized workshops with fixed, clearly defined cleaning areas that require standardized, traceable cleaning
management. Fixed cleaning points need to be planned to cover a stable operating radius. Fixed installation, 25-meter flexible hose coverage, and
intelligent data recording features make it suitable as the primary equipment for after-shift cleaning in workshops.
II. Core Configuration Principles
The following core principles should be followed during the initial planning stage:
1. Prioritize Coverage Radius:
The effective operating radius of the foam cleaning machine is the primary basis for its placement. Intelligent foam cleaning machines (such as the
EFC-325E) come standard with a 25-meter high-pressure hose. Theoretically, a single unit, with a 25-meter hose radius, can cover a circular area of approx
imately 2000 square meters. However, the actual coverage area will be significantly reduced due to workshop pillars, partitions, and equipment layout.
2. Hygiene Zoning Management:
Workshops are typically divided into clean work areas, semi-clean work areas, and general work areas. Different areas have different requirements for
cleaning frequency and standards. Priority should be given to covering clean work areas (such as inner packaging rooms and cooling rooms) and
semi-clean work areas (such as heat processing rooms and cutting rooms), as these areas are key areas for microbial control and cross-contamination
prevention.
3. Flow and Efficiency:
Cleaning points should be located near passageways, pillars, or partition walls to avoid impacting the main production space and material flow while
conveniently covering multiple adjacent areas.
4. Infrastructure Matching:
Each cleaning point requires access to a water source (cold/hot water), power supply, and compressed air (depending on the equipment model). The
accessibility and cost of these pipelines must be considered during planning.
5. Future Development Considerations: The cleaning system should have a certain degree of scalability to accommodate future capacity expansion or
production line adjustments.
Assuming a 5000 sq m workshop is divided into a raw material processing area, a core processing area, an inner packaging cleaning area, and an outerpackaging and storage area.
Option A (Focusing on Fixed Coverage):
01-EFC-325E (3 units):
Fixedly installed on the partition wall between the raw material processing and processing areas, next to the central pillar in the core processing area, and
next to the entrance wall of the inner packaging cleaning area.
02-EFC-325M (1 unit):
Used as a mobile device to cover the outer packaging storage area, assist in changing room cleaning, and serve as a backup and
in-shift cleaning tool for each area.
Option B (Focusing on Flexibility and Initial Investment):
01-EFC-325E (2 units):
Fixedly installed in the core processing area and the inner packaging cleaning area, respectively.
02-EFC-325M (2 units):
One unit handles the raw material processing area and part of the storage area; the other serves as a mobile unit for the entire workshop, used for in-shift
cleaning, covering hard-to-reach areas, and emergency response.
For a 5000 square meter food workshop, the most reasonable configuration is a combination of EFC-325E and EFC-325M.
The EFC-325E serves as the primary unit, responsible for large-area, regular post-shift deep cleaning and disinfection, achieving standardized and
traceable hygiene management.
The EFC-325M serves as an auxiliary and supplementary unit, providing unparalleled mobility to handle complex layouts, in-shift cleaning, and emergency
needs, improving the overall resilience and efficiency of the cleaning system.
The final specific configuration quantity needs to be determined based on the detailed floor plan of the workshop, production process flow, and hygiene
zoning (clean area, semi-clean area).
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————----——————————---------------